Notable features
- Type of writing system: syllabic alphabet consisting of 44 basic consonants, each with an inherent vowel: [o] in medial position and [a] in final position. The [a] is usually found in words of Sanskrit, Pali or Khmer origin while the [o] is found native Thai words. The 18 other vowels and 6 diphthongs are indicated using diacritics which appear in front of, above, below of after the consonants they modify.
- Direction of writing: left to right in horizontal lines.
- 8 of the letters are used only for writing words of Pali and Sanskrit origin.
- For some consonants there are multiple letters. Originally they represented separate sounds, but over the years the distinction between those sounds was lost and the letters were used instead to indicate tones.
- Thai is a tonal language with 5 tones. The tone of a syllable is determined by a combination of the class of consonant, the type of syllable (open or closed), the tone marker and the length of the vowel. More details.
- There are no spaces between words, instead spaces in a Thai text indicate the end of a clause or sentence.
Consonants (พยัญชนะ)

A recording of the Thai alphabet by ปัณณวิช ตันเดชานุรัตน์ (Pannawit Tandaechanurat)
Notes
- Consonants are divided into three classes: low (เสียงต่ำ), mid (เสียงกลาง) and high (เสียงสูง) , which help to determine the tone of a syllable.
- The sounds represented by some consonants change when they are used at the end of a syllable (indicated by the letters on the right of the slash). Some consonants can only be used at the beginning of a syllable.
- Duplicate consonants represent different Sanskrit and Pali consonants sounds which are pronounced identically in Thai.
- The letter o ang acts as a silent vowel carrier at the beginning of words that start with a vowel.
- The names of the consonants are acrophonic and intended to help with learning them.
Vowel diacritics (รูปสระ)

Numerals (ตัวเลขไทย)

A recording of these numbers by ปัณณวิช ตันเดชานุรัตน์
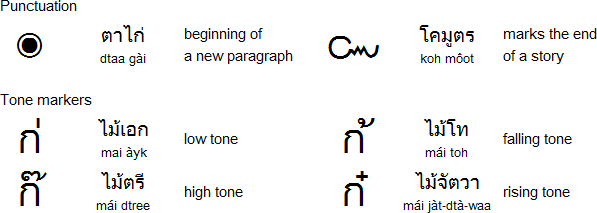
A recording of the Thai tone marker names by ปัณณวิช ตันเดชานุรัตน์
Tone indication
| Tone | Example |
|---|---|
| mid tone (เสียงสามัญ) | ไมล์ [mai] - mile |
| low tone (เสียงเอก) | ใหม่ [mài] - new, again |
| falling tone (เสียงโท) | ไม่ [mâi] - no, not |
| high tone (เสียงตรี) | ไม้ [mái] - wood |
| rising tone (เสียงจัตวา) | ไหม [măi] - question particle / silk |
The tone of a syllable is determined by a combination of the following factors:
- The type of vowel: short or long
- Short vowels are found in syllables with no written vowel (e.g. นม); those ending in -ะ (e.g. โต๊ะ); those with the -็ mark (e.g. เป็น); and those with -ั , -ิ , -ึ or -ุ.
- Other vowels are long.
- NB: "short" here means "short in the context of the tone rules" and such vowels are not necessarily pronounced short.
- The type of syllable: open (คำเป็น) or closed (คำตาย)
- Open syllables end with m, n, ɳ or a long vowel.
- Closed syllables end with p, t, k or a short vowel
- The class (low, middle or high) of the syllable
- The class of a syllable is usually that of the first consonant, unless the first consonant has no vowel mark, or the second consonant is a sonorant, e.g. สลบ pronounced: [สะหฺลบ]
-
- The tone marker
- When a tone marker is used it is placed on the last initial consonant.
Summary of Thai tone rules 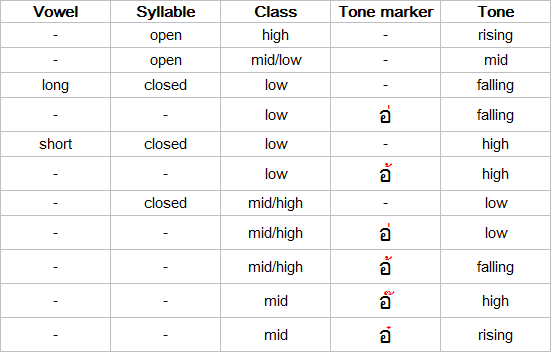
Sample text in Thai

Transliteration
Rao túk kon gèrt maa yàang ìt-sà-rà, rao túk kon mee kwaam kît láe kwaam kâo jai bpen kŏng rao ayng. Rao túk kon kuan dâi ráp gaan bpà-dtì-bàt nai taang dieow gan.Transliteration by http://www.thai2english.com/online/Translation
All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.
(Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights)Thai alphabet for Sanskrit
These are the Thai letters used to write Sanskrit.
Some of the writing systems used to write Sanskrit
No comments:
Post a Comment